...
Kubernetes, also known as K8s, is an open-source system for automating deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. If you are not familiar with K8s, see Kubernetes Tutorial presented at a SDSC event in 2022 where you can find relevent slides. There are also some useful introduction materials provided by IBM: 1) Docker and 2) Kubernetes, and those presented by Red Hat: 1) What's a Linux container? and 2) What is Kubernetes?
Step
...
0. Prerequisites
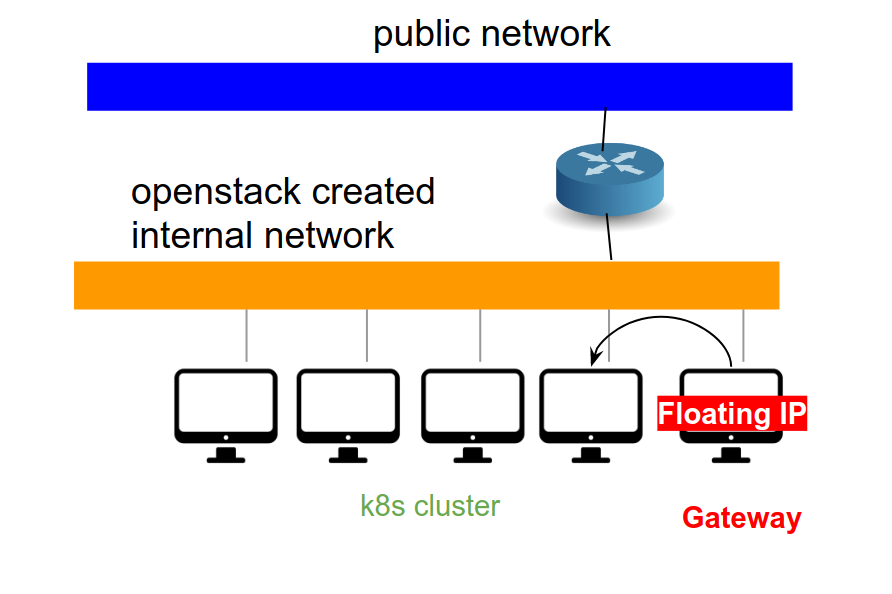 Image Added
Image Added
- It is best to work from the gateway node of your project, i.e., we assume that you will have a direct network connection to each k8s nodes.
- It seems best to use the openstack cli whenever possible (e.g., to generate kube config files).
- To use the openstack cli commands, you need to setup the envirments. You can download the rc file from the openstack dashboard (API access → Download OpenStack RC file → OpenStack RC file )
- Download the rc file to the gateway node.
| Code Block |
|---|
| language | bash |
|---|
| theme | Midnight |
|---|
| title | Setup the openstep rc |
|---|
| linenumbers | true |
|---|
|
# the name of the rc file will reflect your project name. In this case, the project name is 'spherex'
> source spherex-openrc.sh # this will ask for a password. Use the same password that you use for the dashboard.
# The rc file need to be loaded before you use openstack cli tools. |
| Code Block |
|---|
| language | bash |
|---|
| theme | Midnight |
|---|
| firstline | 1 |
|---|
| title | setup kube config |
|---|
| linenumbers | true |
|---|
|
# somehow, openstack cli packages from ubuntu does not work. Instead, we install them via pip command.
> sudo apt-get install python-dev python3-pip # install pip
> sudo pip install python-openstackclient python-magnumclient
# depending on what you want to do with openstack cli, you may need to install other packages. For our purpose, magnum client should be sufficient. |
- You need to generate a k8s cluster template. This must be done per project basis.
- You can follow the instruction here Note that a separate cluster template for k8s needs to be created for each project. (참조 : k8s template creation guide (in Korean)) or use the shell script below and customize.
| Code Block |
|---|
| language | bash |
|---|
| theme | RDark |
|---|
| title | create-k8s-template.sh |
|---|
| linenumbers | true |
|---|
|
TEMPLATE_NAME=k8s-spherex-test20
NETWORK_NAME=spherex-network
SUBNET_NAME=spherex-subnet
KEYPAIR=spherex-gw-ubuntu01
# DNS=8.8.8.8
DNS=210.110.233.74
LABELS="ingress_controller=octavia,cinder_csi_enabled=true,auto_healing_enabled=false,auto_scaling_enabled=false,availability_zone=nova"
# LABELS="auto_healing_enabled=false,auto_scaling_enabled=false,availability_zone=nova"
openstack coe cluster template create $TEMPLATE_NAME \
--coe kubernetes \
--image fedora-core-32 \
--external-network public \
--fixed-network $NETWORK_NAME \
--fixed-subnet $SUBNET_NAME \
--network-driver calico \
--dns-nameserver $DNS \
--floating-ip-disabled \
--master-flavor C8M16D40 \
--flavor C8M16D40 \
--keypair $KEYPAIR \
--volume-driver cinder \
--docker-storage-driver overlay \
--docker-volume-size 20 \
--labels $LABELS
|
- You should change the NETWORK_NAME and the SUBNET_NAME for your project.
- "TEMPLATE_NAME" is the name of the template that will be created. Give a sensible name.
- "KEYPAIR" is the name of the ssh key pair you registered. You may use the public key of you account at the gateway node.
- "DNS": 210.110.233.74 is the internal dns we manages and have a entry to internal domain names (.e.g, registry.kasi.re.kr)
- "LABELS" : we will activate octavia ingress controller and cinder csi (to provision persistent volume)Use "Calico" as a network driver. "flannel" seem to have a issue.
- It is handy to have a ingress controller. Add a label of 'ingress_controller="octavia"' to enable the octavia ingress controller. Other type of ingress controllers are not tested yet.
- In-tree cinder csi seems to have a limited capability. It seems best to use the out-of tree csi driver (which will be enabled by the label of "cinder_csi_enabled=true".
- You can adjust most of the parameters while you create the cluster. However, I was advised that, for the "LABEL", it is best to set it in the template and not to customize during the creation.
- Currently, it will create a template with a single master node (no HA).
- Use "Calico" as a network driver. "flannel" seem to have a issue.
Step 1. Create a Kubernetes (k8s) cluster
- From the Container Infra section, use the template to create the k8s cluster of the size you want.
- Use the existing network andkeep cluster api private.
- A single master is only configured and tested for now.
- You can add additional worker nodes later (you can delete some of them), but I don't think you not sure we can change the flavor of the nodes.
- creating a k8s cluster may take tens of ~ 10 minutes and it may fail sometime. Just delete the failed one and recreate one.
- The ssh key-pair is usually not important. Just use the default.
- My recommendation is to create the cluster of a single worker. Once completed, resize the cluster for your needs.
- Often, the cluster creation become pending during the worker node creation ("in progress" even after 15 minutes). Log in to the worker node (id:core), and try to restart the "heat-container-agent.service" (sudo systemctl restart heat-container-agent.service). Check the status of the service and make sure it is active and running. Once this is done, the cluster creation will proceeds and complete within a few minutes
Use the existing network and keep cluster api private- Note that a cluster will be also be created under the Cluster Infra → KASI cluster section.
| Fig. 1-1 General setup tab for creating k8s from template | Fig. 1-2 "size" tab |
|---|
| |
...
| Fig. 1-3 "Network" tab | Fig. 1-4 "Management" tab | Fig. 1-5 "Advanced" tab |
|---|
| | |
- Once created, go ahead and resize the cluster (use the "resize" in the dropdown menu of created cluster).
| Fig. 1-6: resize the cluster |
|---|
 Image Added Image Added
|
Step 2. Setup connection to the created k8s cluster
- It is best to work We assume that you are working from the gateway node of your project, i.e., we assume that you have a direct network connection to each k8s nodes.It seems that it is best to use the openstack cli to generate kube config files.
- To use the openstack cli commands, you need to setup the envirments. You can download the rc file from the openstack dashboard (API access → Download OpenStack RC file → OpenStack RC file )
Download the rc file to the gateway node.- Make sure you have "kubectl" command installed on the gateway : https://kubernetes.io/ko/docs/tasks/tools/install-kubectl-linux/
- load the rc environments if you have not done yet.
| Code Block |
|---|
| language | bash |
|---|
| theme | Midnight |
|---|
| title | Setup the openstep rc |
|---|
| linenumbers | true |
|---|
|
# the name of the rc file will reflect your project name. In this case, the project name is 'spherex'
> source spherex-openrc.sh # this will ask for a password. Use the same password that yo use for the dashboard.
# The rc file need to be loaded before you use openstack cli tools |
| Code Block |
|---|
| language | bash |
|---|
| theme | Midnight |
|---|
| firstline | 1 |
|---|
| title | setup kube config |
|---|
| linenumbers | true |
|---|
|
# somehow, openstack cli packages from ubuntu does not work. Instead, we install them via pip command.
> sudo apt-get install python-dev python3-pip # install pip
> sudo pip install python-openstackclient python-magnumclient
# now it's time to fetch the kube config for your cluster
> openstack coe cluster config YOUR-K8S-CLUSTER-NAME
# The above command will create a file named "config" under the current directory. This is basically a kube config file that you can use with kubectl command.
# You may environment variable of "KUBECONFIG" to this file, as suggested by the above command. You may instead copy this file under "~/.kube" |
...
| Code Block |
|---|
| language | yml |
|---|
| theme | Midnight |
|---|
| title | sc-cinder-yaml |
|---|
| linenumbers | true |
|---|
|
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1beta1v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
name: standardcinder-default
annotations:
storageclass.beta.kubernetes.io/is-default-class: "true"
labelsprovisioner:
kubernetes.io/cluster-service: "true"
addonmanager.kubernetes.io/mode: EnsureExists
provisioner: kubernetes.io/cinder
cinder.csi.openstack.org
|
- Once you have a file with above contents (the file is named as 'sc-cinder.yaml' in this example)
| Code Block |
|---|
| language | bash |
|---|
| theme | Midnight |
|---|
| linenumbers | true |
|---|
|
> kubectl apply -f sc0cindersc-cinder.yaml
> kubectl get storageclass
NAME PROVISIONER RECLAIMPOLICY VOLUMEBINDINGMODE ALLOWVOLUMEEXPANSION AGE
standardcinder-default (default) kubernetes.io/cindercinder.csi.openstack.org Delete Immediate false 7d1h
|
Step 4. Deploy your app
...
simple example with Helm 3
...






